… by JG Bhuvanesh, Business Line Manager – Industrial Assembly Solutions, Industrial Technique, Atlas Copco (India)
Today, the body-in-white stage represents a critical point in modern automotive manufacturing for defining the structural integrity of a vehicle. At this stage, sheet metal components are combined into a chassis. This forms the basis for crash performance, vehicle rigidity, noise, vibration, and long-term durability. With automakers’ unending quest for lighter, safer, more efficient vehicles, adhesive dispensing has emerged as one of today’s most important technologies for the assistance of traditional welding and mechanical fastening techniques.
Evolving Challenges in the Body Shop
Modern cars have a mixed material approach for reducing weight while not sacrificing safety. The use of many different types of materials introduces some challenges when they are bonded together because the adhesive must provide strength and stability between them. Corrosion resistance at hem flange joints is another requirement for any adhesive used to bond different types of automotive components. Furthermore, adhesives need to be durable and able to perform under repeated dynamic forces.
A critical additional requirement of adhesive solutions is to dampen the effect of noise, etc., by providing an elastic bond where they connect. Historically, certain automobile body parts, such as doors, roofs, rear-end structures, or compartments, have been made with a rigid connection. Under the current assembly requirements for automobile manufacturers, there is not enough time available to assemble vehicles using this method. Therefore, adhesive solutions need to be both accurately constructed and to hold their accuracy consistently over high-volume production.
Adhesive Applications Across Key Body Shop Processes
Automotive body shops apply adhesives in various processes, each with unique technical requirements:
- Roof structures: Roof structures are designed to meet high aesthetic and functional standards, including noise reduction and insulation. Made from materials like aluminum, steel, plastic, or carbon, each with unique properties, the challenge is to ensure a stable, durable, and high-performance structure.
- Framing: Framing joins the side walls with the roof frame and underbody, focusing on crash safety, lightweight design, and short production times. Customized bonding solutions enhance crash safety while minimizing weight.
- Closure parts: Closure parts like doors, hoods, and bumpers create stable connections between components, optimizing crash safety, vehicle rigidity, and corrosion protection. Seam bonding is a complex technique used in this process.
- Underbody: The underbody forms the basis for key vehicle components like the chassis and engine, requiring a strong structure. This is achieved by joining different materials using techniques like bonding and spot welding. Ensuring a safe and healthy working environment is crucial.
Techniques in Modern Adhesive Dispensing
Adhesive application methods have evolved to meet these challenges, with several techniques gaining prominence:
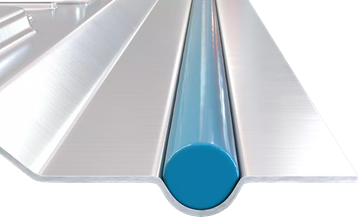
- Bead application: The adhesive beads are spaced evenly in an elongated form, as the adhesive is required to bond in a controlled manner, especially on flat surfaces.
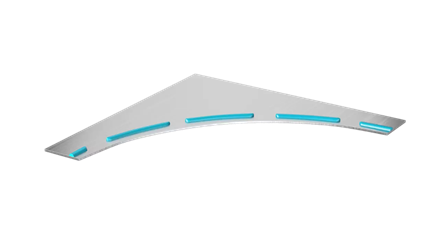
- Stitch bead application: The adhesives are applied in select areas or in intervals in order to save adhesive and make bonds stronger at specific points.
- Swirl application: The adhesive is applied in circular or swirl motions. This type of application takes place when one wants to apply adhesive over large portions, hence it is very effective in adhesive bonding processes. This is most helpful when applying adhesive on irregularly shaped surfaces.
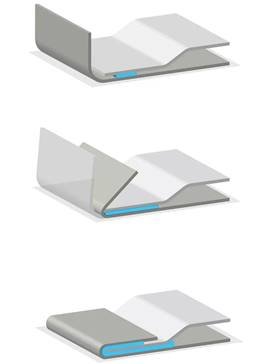
- Multi-Dot application: This process uses small dots of adhesives to cover the surface. This method of applying adhesives has good control over positioning and amount and is ideal for applications requiring precision.
Each technique has advantages depending on the component geometry, load requirements, and production speed. High-volume manufacturing also demands systems capable of precise dosing and repeatable performance. As vehicle architectures have moved towards lightweight platforms, electric vehicles, and modular body designs, adhesive dispensing has become more of a strategic enabler to manufacturers than just a complementary joining process. Currently, adhesives have been expected to perform multiple functions: as structural reinforcers, sealers, anti-vibration dampeners, and corrosion protectors, and to accomplish all of these different types of functions with one application of adhesive, decreasing the number of components needed for the assembly and supporting flexible manufacturing systems.
Structural, Sealing, and Anti-Flutter Applications
- Structural Bonding: By providing support to joints to withstand stress, structural adhesive bonding enhances the safety of vehicles in a crash, holds them rigid, and allows them to be made lighter. The processes involve framing, underbody components, and attaching supplemental components.
- Sealing: Seals provide a barrier against water, air, and contamination. This helps create a corrosion-resistant and NVH-performant joint. The precision bead application is very important for a complete fill.
- Anti-Flutter: Doors, hoods, and trunk lids need elastic bonding to prevent resonant oscillations between the inner and outer panels. Methods of multi-dot or elastic bead application can be regarded as damping mechanisms for sound and maintaining panel integrity.
Trends Shaping Adhesive Dispensing in Automotive Manufacturing
Several trends are transforming the role of adhesives in body shops:
- Lightweighting: Adhesives have made the bonding of mixed materials possible without adding mass, hence supporting fuel efficiency and EV battery range.
- Automation & Cobots: Automated distribution systems and cobots ensure precision, reduce cycle time, and enhance repeatability.
- Sustainability: Adhesives with low environmental impact, recyclable materials, and energy-efficient curing processes are becoming of increasing importance.
- Advanced Testing & Simulation: Digital solutions let engineers compute the structure for stress distribution, curing time, and NVH performance to optimize the usage of adhesives before production.
In addition to increased productivity, a controlled adhesive dispensing system also contributes to sustainability efforts. This is achieved through reduced material use, less exposure to the material for the operators, and a cleaner production environment. This is important as OEMs move towards embracing global standards in production.
Supporting Innovation in Adhesive Dispensing
Although there is rapid technological development for high-performing adhesive technology, the necessity to apply this technology requires specialized competency as well as validation and optimization. Manufacturers such as Atlas Copco are developing very advanced technology to dispense adhesives and provide expert advice to manufacturers in order to improve the quality and efficiency of the manufacturers’ manufacturing processes, validate the adhesive materials and technologies being used, and maximize efficiency and effectiveness in the operation of their factories.











